STD: Stable Triangle Descriptor for 3D place recognition
Abstract
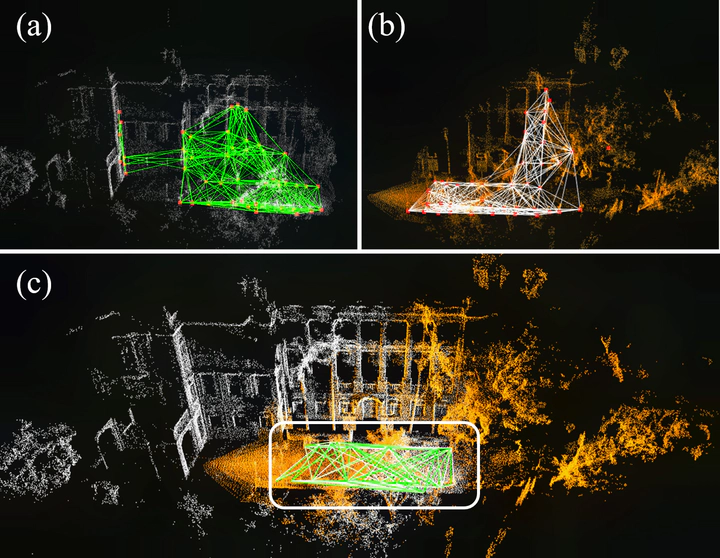
In this work, we present a novel global descriptor termed stable triangle descriptor (STD) for 3D place recognition. For a triangle, its shape is uniquely determined by the length of the sides or included angles. Moreover, the shape of triangles is completely invariant to rigid transformations. Based on this property, we first design an algorithm to efficiently extract local key points from the 3D point cloud and encode these key points into triangular descriptors. Then, place recognition is achieved by matching the side lengths (and some other information) of the descriptors between point clouds. The point correspondence obtained from the descriptor matching pair can be further used in geometric verification, which greatly improves the accuracy of place recognition. In our experiments, we extensively compare our proposed system against other state-of-the-art systems (i.e., M2DP, Scan Context) on public datasets (i.e., KITTI, NCLT, and Complex-Urban) and our self-collected dataset (with a non-repetitive scanning solid-state LiDAR). All the quantitative results show that STD has stronger adaptability and a great improvement in precision over its counterparts. To share our findings and make contributions to the community, we open source our code on our GitHub: https://github.com/hku-mars/STD.
Introduction
STD is a global descriptor for 3D place recognition. For a triangle, its shape is uniquely determined by the length of the sides or included angles. Moreover, the shape of triangles is completely invariant to rigid transformations. Based on this property, we first design an algorithm to efficiently extract local key points from the 3D point cloud and encode these key points into triangular descriptors. Then, place recognition is achieved by matching the side lengths (and some other information) of the descriptors between point clouds. The point correspondence obtained from the descriptor matching pair can be further used in geometric verification, which greatly improves the accuracy of place recognition.

Related video
Our accompanying video is now available on YouTube.
